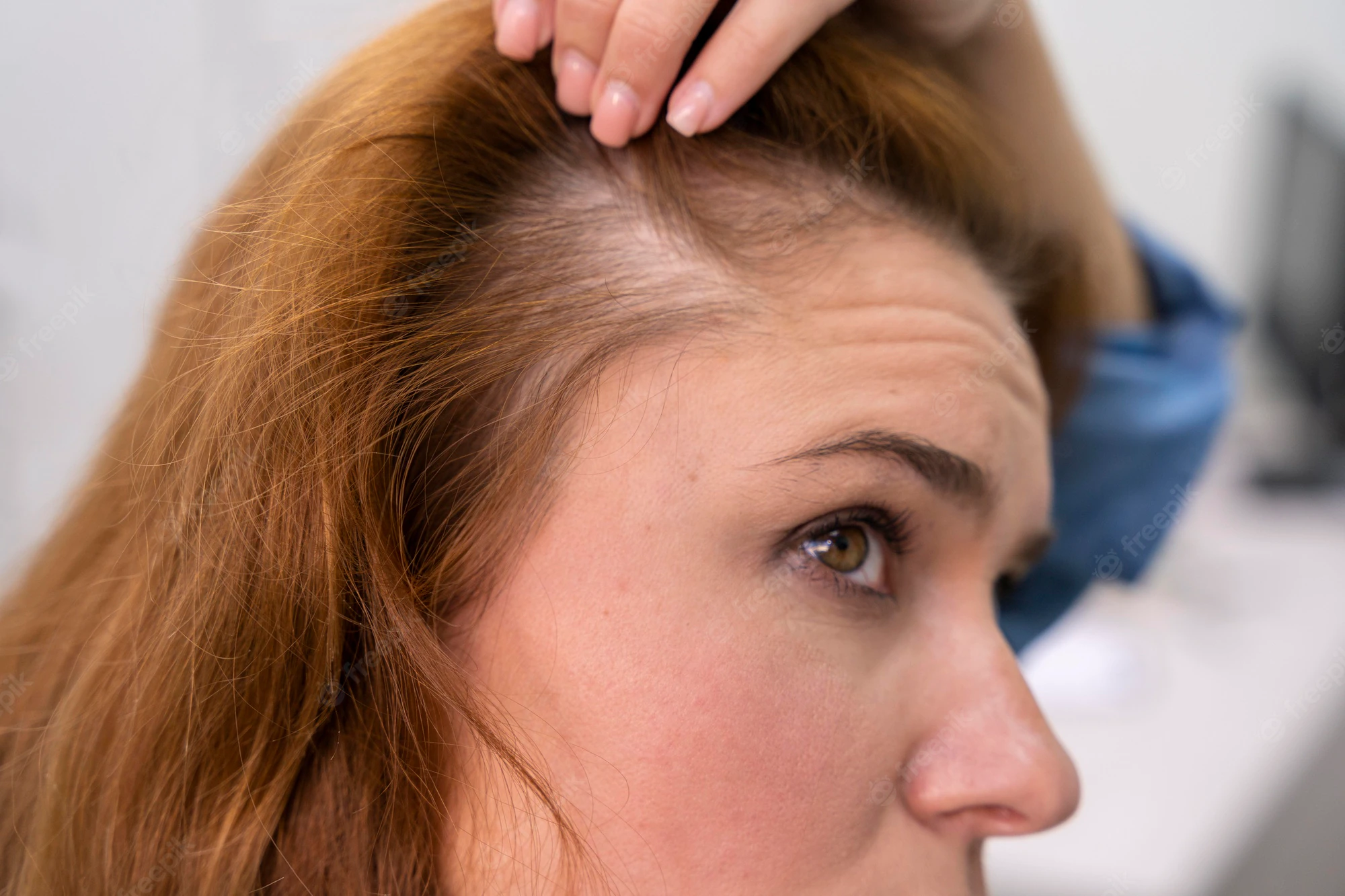
We often eat according to what we feel and the food we eat affects the way we feel! We often fill our body with food when we are hungry and in order to be satisfied, feelings of hunger pleasure and fulfillment needs to be met. Understanding the reason of food choices with the psychology of eating is really important and it depends on the following factors. So, let’s dive in the factors before getting any late. Have a look!
Also read: Probiotics Might Help In Treating Bipolar Disorder; 10 Super Healthy Probiotic Foods
Some of the important factors:
1. The Hunger Hormones (Leptin and Ghrelin)
Most of us didn’t know that there are hormones in our body, with the chief job to make us feel hungry. Leptin is the hormone known as appetite suppressor and made in fat cells which decreases our appetite, and suppresses the food intake, thereby inducing weight loss. Ghrelin is another hormone which stimulates the hunger by entering the brain and acts on the neurons in the hypothalamus to increase the activity of the hunger-causing nerve cells and thereby reducing the activity of hunger-inhibiting cells. The level of these hormones typically rises before a meal, when our stomach is empty and then decrease shortly after, when our stomach is full. That’s how, these hormones play a major role in hunger, appetite, and food intake. But by having a sustainable and enjoyable diet plan you can avoid large fluctuations in weight and these hunger hormones.

We often eat according to what we feel and the food we eat affects the way we feel!
Photo Credit: iStock
2. The Happy Hormones (Serotonin and Tryptophan)
Serotonin hormone drives our mood, behavior and energy levels. It also stimulates feelings of happiness and positivity. This hormone is synthesized from tryptophan, which is an amino acid found in foods like milk, tofu, soy, peanuts and chocolates that aims to boost our happy hormone levels. In fact, right amount of tryptophan is also used to treat insomnia, depression, anxiety and general mood disorders.
3. Low-Carb Diet May Affect The Brain Function
Before understanding what low carb diet actually is, people try to attempt it and end up messing the whole thing by experiencing the hidden dangers of low carb diet and eventually hurting their bodies. Our body breaks carbohydrates into glucose which in term used as a fuel for brain activity. Eliminating carbohydrates from the diet might also reduce the brain’s source of energy and affect its function. Hypoglycemia can also occur to those who drastically cut the high carbs diet which can leads to headache, nausea, anxiety and brain fog. Good sources of complex carbohydrates should be included in our diet instead of simple carbs which is found in starchy foods like bananas, brown rice, chickpeas, lentils and whole grains.
3. Low Fat Diet Also Affects The Brain Function
Cholesterol and saturated fats is vital for well-functioning of the brain. Cholesterol functions as a brain defensive antioxidant. It is the raw material from which our bodies make vitamin D, and in addition to that cholesterol also precursor the sex hormones estrogen, progesterone and testosterone all of which contribute to the healthy brain function. Saturated fat is also one of the main components of brain cells, and it also provides benefits to the liver and immune system and also helps to maintain proper hormonal balance.
4. D and Omega 3 for Mental Health
Vitamin D and Omega 3 works together to improve cognitive function and social behavior with particular relevance to overall mental health. Omega 3 acid promotes healthy blood flow, which is essential to optimal brain function. Vitamin D also helps to control the immune system and the release the hormones like dopamine and serotonin. These hormones affect the brain function and its development while consequently, improving your mental health. Vitamin D has been found also in the regions of the brain which is linked to depression. Other than fish, omega 3 rich sources are soya beans, walnuts and chia seeds. Fatty fish, like tuna, mackerel, and salmon are rich in vitamin D and the vegetarian sources of vitamin D, can be dairy products, orange juice, soy milk, and cereals.
[“source=ndtv”]